10 bronchitis symptoms
 Article Sources
Article SourcesBronchitis occurs when the bronchial tubes are inflamed. These tubes are what allows air to travel into the lungs, and when they’re inflamed, it can be more difficult for a person to breathe.[[1]] Mucus also develops in the airways, which can lead to symptoms such as coughing. Bronchitis can be acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis typically improves within 10 days, while chronic bronchitis never goes away completely.[[1]] Both acute and chronic bronchitis can be uncomfortable. In some cases, it can be a serious condition that impacts breathing. Acute bronchitis is often caused by viruses such as flu, SARS-CoV-2, or the common cold.[[2]] Understanding the symptoms of bronchitis can help individuals know when they should seek medical treatment for their condition.
Cough
Inflammation of the airways and the development of mucus cause irritation that leads to an ongoing cough. Many times, bronchitis symptoms include a cough that is productive, which means it brings up mucus.[[2]] In some cases, the cough may begin as a dry cough and later develop into a productive cough.[[3]] The cough may worsen at night.[[5]] A cough caused by bronchitis can last for some time. In cases of acute bronchitis, coughs can last on average 2 to 3 weeks before tending to resolve on their own.2 However, a case of chronic bronchitis leads to productive coughing that lasts 3 months or more.[[2]]

Advertisement
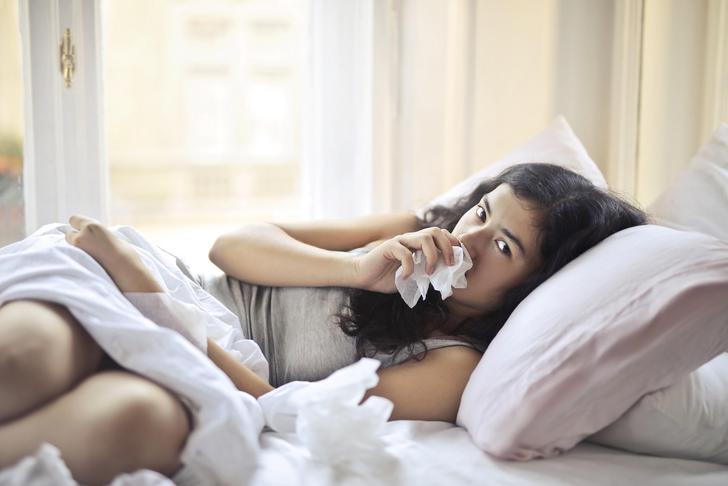
Clear or Yellow Sputum
Typically, someone who has a cough that is bronchial in nature will bring up sputum, or mucus, at least some of the time when they cough. In cases of acute bronchitis, it’s likely that the sputum will be clear or yellowish.[[4]] In some cases, mucus may be thicker or green. This is not necessarily a sign of bacterial infection and, therefore, does not automatically mean antibiotics should be prescribed.[[4]] Ultimately, a course of action should be determined by a qualified medical professional after an evaluation of the patient and all the symptoms.

Advertisement
Sore Throat
Bronchitis can lead to irritation in the throat. This is often caused by all the coughing and the presence of mucus. Some people describe this irritation as a tickling in their throat. As the condition progresses, the irritation can lead to a sore throat.[[5]] In more severe cases, the sore throat can cause someone to not want to eat or drink because it is uncomfortable to swallow. They may also favor soft or cold foods during this time.

Advertisement
Runny Nose
It is common for someone with acute bronchitis to experience other signs and symptoms of upper respiratory infections. That can include a runny nose or other symptoms of mucus in the sinuses, such as having to blow their nose a lot.[[4]] Congestion and other mucus-related symptoms of bronchitis can be worse at night or in the morning. This is because the mucus can settle overnight and needs to be cleared out in the morning.

Advertisement
Discomfort in the Chest
Bronchitis can cause pain or tightening in the chest.[[2]] While a feeling of mild tightness in the chest might be common with bronchitis, individuals should always take these symptoms seriously and consult medical professionals. The majority of chest pain reported in emergency rooms in the United States is not related to cardiac issues.[[6]] However, because individuals cannot tell if the chest pain is due to a heart condition, seeking medical attention early can help diagnose and manage serious cardiac episodes if they are the underlying cause of chest discomfort.

Advertisement
Low Fever
A low-grade fever is common with acute bronchitis. Fevers below 100.4 degrees F are not typically concerning with bronchitis and can often be treated in the home.[[2]] A low fever can lead to some other mild symptoms. Those can include minor joint and muscle aches and pains, which can also often be treated with home remedies such as soaking in a bath or taking over-the-counter medications.

Advertisement
Wheezing
Wheezing occurs when the airways are partially blocked.[[7]] Individuals who have wheezing may find it somewhat hard to breathe or feel like they are breathing through something thicker than normal air. Wheezing also typically causes a whistling sound when someone breathes. This sound can be very slight and hard to hear, or louder and apparent to anyone nearby.

Advertisement
Squeaky Breathing
Aside from traditional wheezing, bronchitis may cause other sounds when someone breathes. This can include a whistling or squeaky-sounding breathing.[[8]] These sounds may be caused by the same thing that causes traditional wheezing. They are caused by a buildup of mucus in various parts of the airways. In this case, clearing the mucus may lead to reduced sounds when breathing.

Advertisement
Fatigue
As with many illnesses, bronchitis can lead to tiredness or fatigue.[[2]] Individuals may find they have to take breaks when doing physical activities, such as cleaning the house. Fatigue can last weeks with acute bronchitis and months with chronic bronchitis.

Advertisement
Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath is an inability or seeming inability to pull in an entire breath. Someone experiencing this symptom may feel like they are out of breath even if they are not performing physical activity. With bronchitis, shortness of breath may be triggered by cold air or strong odors.[[9]] This is because these types of environmental factors can cause bronchial tubes to narrow briefly. If the bronchial tubes are already inflamed, this narrowing can make it even harder for air to pass through. Someone who is having trouble breathing should consult medical professionals because this symptom can also be caused by serious heart or lung conditions.

Advertisement