Understanding Dizziness: 10 Common Causes
Dizziness is a common symptom that can be caused by a variety of factors. It is important to understand the potential causes of dizziness in order to properly address the issue and seek appropriate treatment. In this article, we will explore 10 common causes of dizziness.
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, leading to an imbalance in the body’s electrolytes. This can cause dizziness, as well as other symptoms such as thirst, dry mouth, and fatigue[[2]].

Advertisement
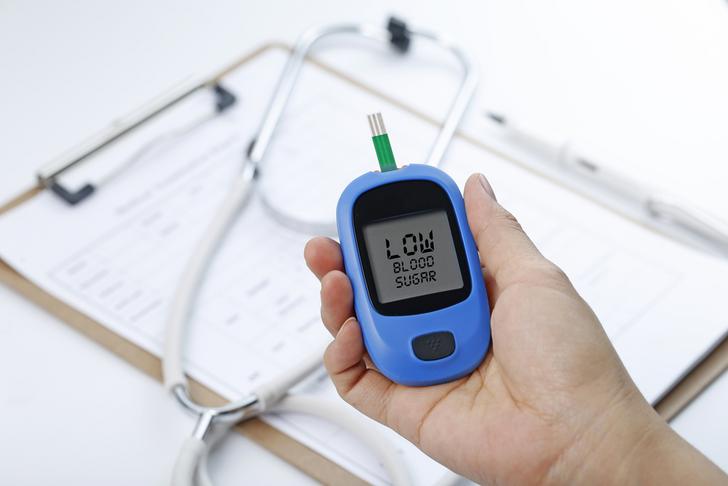
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can cause dizziness, along with symptoms such as shakiness, sweating, and confusion[[3]]. Hypoglycemia is most commonly associated with diabetes, but it can also occur in people without diabetes due to certain medications, excessive alcohol consumption, or skipping meals.
Advertisement
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
BPPV is a common inner ear disorder that causes brief episodes of dizziness, usually triggered by changes in head position. It occurs when small calcium particles in the inner ear become dislodged and move into the semicircular canals, disrupting the balance system[[4]].

Advertisement
Labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis is an inflammation of the inner ear, often caused by a viral or bacterial infection. This condition can cause dizziness, vertigo, and problems with balance and hearing[[5]].

Advertisement
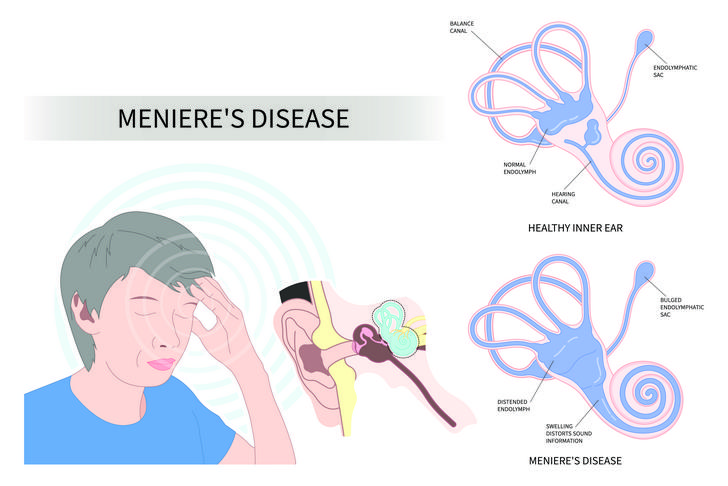
Meniere’s Disease
Meniere’s disease is a chronic inner ear disorder that causes episodes of vertigo, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), and hearing loss. The exact cause of Meniere’s disease is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an abnormal buildup of fluid in the inner ear[[6]].
Advertisement
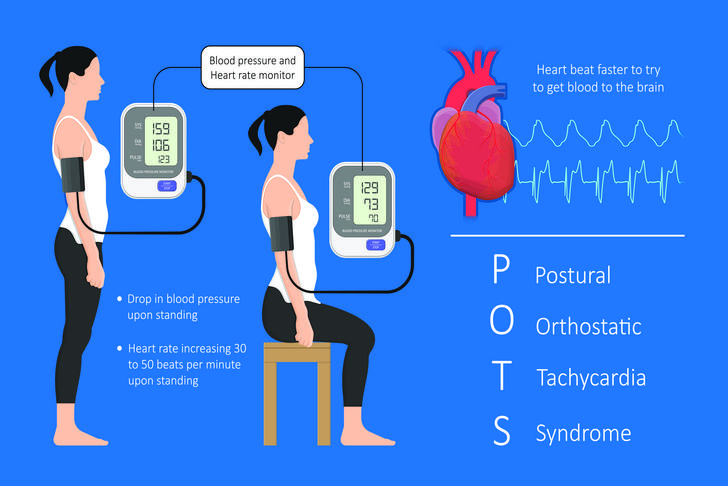
Orthostatic Hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a sudden drop in blood pressure that occurs when a person stands up from a sitting or lying position. This can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, and even fainting[[7]].
Advertisement
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to its tissues. This can cause dizziness, as well as fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath[[8]].
Advertisement
Migraines
Migraines are a type of headache characterized by severe pain, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Some people with migraines also experience dizziness or vertigo, known as vestibular migraines[[9]].

Advertisement
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Generalized anxiety disorder is a mental health condition characterized by excessive and persistent worry about various aspects of life. People with GAD may experience dizziness as a symptom of their anxiety, along with other physical symptoms such as muscle tension, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating[[10]].

Advertisement
Symptoms of Dizziness
Dizziness is a term used to describe a range of sensations, such as feeling faint, woozy, weak, or unsteady. Dizziness that creates the false sense that you or your surroundings are spinning or moving is called vertigo.
Symptoms that might accompany dizziness include:
- A false sense of motion or spinning (vertigo)
- Lightheadedness or feeling faint
- Unsteadiness or a loss of balance
- A feeling of floating, wooziness, or heavy-headedness
- Blurred vision or double vision
- Confusion or disorientation
Other symptoms might also occur before or during episodes of dizziness, such as:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Sweating
- Abnormal eye movements
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- A feeling of fullness in the ear
- A headache
These symptoms can vary from mild to severe and last from a few minutes to several days, depending on the cause.
Advertisement
Treatments for Dizziness
Dizziness treatments depend on the cause and symptoms. Treatments can involve medications, physical therapy, lifestayle changes, and even surgery. Below are some possible treatments:
Medications: A variety of drugs can help treat dizziness, such as anti-nausea medications, antihistamines, or medications to reduce inner ear inflammation.
Vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT): This form of physical therapy is designed to help improve balance and reduce problems related to dizziness. It’s often used for people with vertigo from inner ear conditions.
Canalith repositioning maneuvers: These are a series of specific head and body movements for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). The movements help move calcium deposits out of the inner ear canals so they can be absorbed by the body.
Lifestyle modifications: This could include changes to diet and physical activity, drinking more fluids to avoid dehydration, limiting caffeine and alcohol, and quitting smoking.
Psychotherapy: If dizziness is related to an anxiety disorder, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) might help.
Surgery or other procedures: If dizziness is caused by a vestibular migraine or Ménière’s disease that doesn’t respond to other treatments, injections or surgery might be an option.
In summary, dizziness is a complex and multifaceted symptom that can be indicative of a wide range of conditions, from the relatively benign to the potentially severe. Recognizing the signs and symptoms associated with dizziness is the first step towards managing it effectively. These symptoms can be as varied as the potential causes and can range from a feeling of lightheadedness to a sensation of spinning, known as vertigo.
Equally important is understanding that treatment for dizziness must be tailored to the underlying cause. Options may span from lifestyle modifications and physical therapy, to medications and, in certain cases, surgery. The choice of treatment strategy depends heavily on an accurate diagnosis, which underscores the critical role of professional healthcare consultation.
To navigate through the challenges posed by dizziness, it is essential to maintain an open dialogue with your healthcare provider, keep them informed about your symptoms, and follow through with the recommended treatment plan. In doing so, you will be well-equipped to manage your dizziness effectively, thereby improving your quality of life and overall well-being.

Advertisement