10 Causes of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide. Understanding the causes of prostate cancer can help in its prevention and early detection. In this article, we will explore 10 factors that contribute to the development of prostate cancer.
Age
Age is the most significant risk factor for prostate cancer. The risk of developing the disease increases with age, particularly after the age of 50. Approximately 60% of prostate cancer cases are diagnosed in men aged 65 or older[[1]].
Advertisement
Genetics and Family History
Men with a family history of prostate cancer have a higher risk of developing the disease. If a man’s father or brother has had prostate cancer, his risk is doubled. The risk is even higher if several close relatives have had the disease, especially if they were diagnosed at a young age[[1]].
Advertisement
Race and Ethnicity
Prostate cancer is more common in certain racial and ethnic groups. African American men have the highest risk of developing prostate cancer, followed by Caucasian men. Asian and Hispanic men have a lower risk of developing the disease[[1]].

Advertisement
Diet
A diet high in red meat, processed meat, and high-fat dairy products may increase the risk of prostate cancer. Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help reduce the risk of developing the disease[[2]].

Advertisement
Obesity
Obesity has been linked to an increased risk of developing aggressive prostate cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise may help reduce the risk of prostate cancer[[3]].

Advertisement
Inflammation
Chronic inflammation in the prostate may contribute to the development of prostate cancer. Inflammation can cause cell damage, which may lead to the formation of cancerous cells[[4]].
Advertisement
Hormones
High levels of androgens, male hormones such as testosterone, may increase the risk of prostate cancer. Some studies suggest that men with higher levels of testosterone may have a higher risk of developing the disease[[5]].

Advertisement
Exposure to Chemicals
Exposure to certain chemicals, such as those used in the rubber and textile industries, may increase the risk of prostate cancer. Men who have been exposed to Agent Orange, a chemical used during the Vietnam War, also have an increased risk of developing the disease[[1]].
Advertisement
Vasectomy
Some studies have suggested that men who have had a vasectomy may have a slightly increased risk of developing prostate cancer. However, more research is needed to confirm this association[[3]].

Advertisement
Sexually Transmitted Infections
There is some evidence to suggest that men who have had a sexually transmitted infection (STI) may have a slightly increased risk of developing prostate cancer. However, more research is needed to confirm this link[[5]].
Advertisement
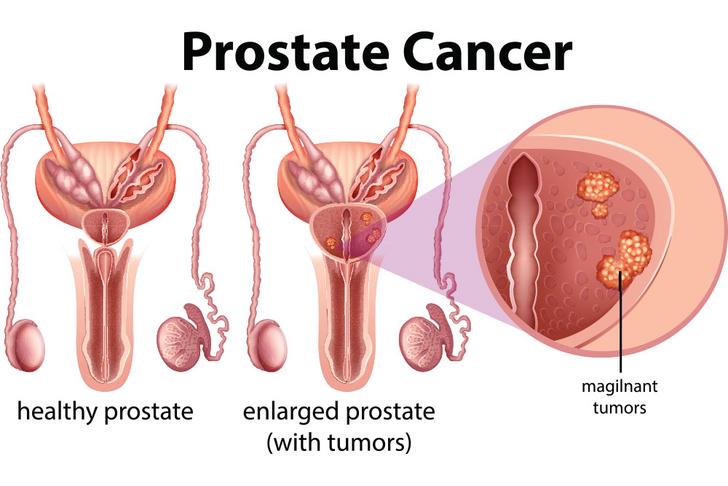
Symptoms
Prostate cancer may not cause any symptoms in its early stages, so regular screening is essential for early detection.
However, as the disease progresses, some common symptoms of prostate cancer may include:
Urinary changes: These can include increased frequency of urination, especially at night (nocturia), difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine flow, or a sense of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Blood in urine or semen: Prostate cancer can cause blood to appear in the urine or semen. However, other non-cancerous conditions can also lead to these symptoms.
Erectile dysfunction: While erectile dysfunction can have various causes, prostate cancer can contribute to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection.
Pain or discomfort: Advanced prostate cancer may cause pain in the back, hips, pelvis, or other areas. This can be due to cancer spreading to nearby tissues or bones.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other non-cancerous conditions, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or urinary tract infections. Nevertheless, if you experience any of these symptoms or have concerns, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Early detection through regular prostate cancer screening, such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood tests and digital rectal exams, remains the most effective way to identify prostate cancer before symptoms arise. If prostate cancer is diagnosed, your healthcare provider will work with you to determine the best treatment options based on the stage and characteristics of the cancer.
Advertisement
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the various causes of prostate cancer can help in its prevention and early detection. While some factors, such as age and genetics, cannot be changed, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, may help reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Advertisement