10 Causes of Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health issue affecting millions of people each year. They occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and cause inflammation, leading to symptoms such as pain, frequent urination, and fever. Understanding the causes of UTIs can help you take steps to prevent them and maintain a healthy urinary system. In this article, we will explore 10 common causes of urinary tract infections.
Sexual Activity
Sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urethra, increasing the risk of a UTI. Women are particularly susceptible due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily. To reduce the risk of UTIs, it is important to practice good hygiene and urinate after sexual activity to help flush out bacteria[[1]].

Advertisement
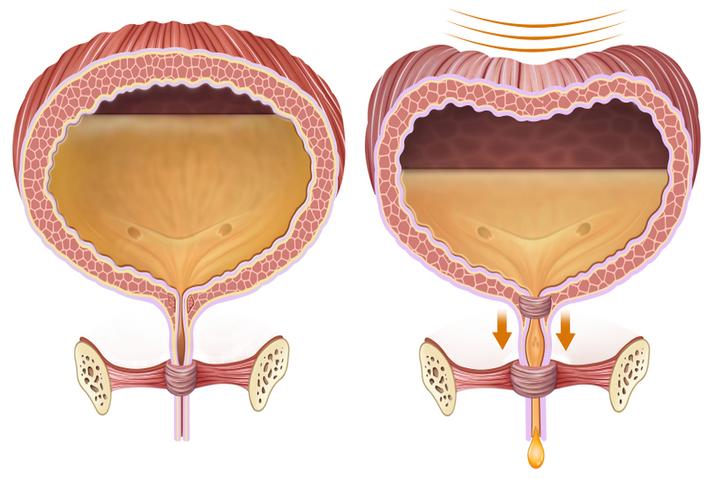
Urinary Retention
Urinary retention, or the inability to completely empty the bladder, can lead to UTIs. This is because stagnant urine in the bladder provides an ideal environment for bacteria to grow. Conditions that can cause urinary retention include an enlarged prostate, nerve damage, or certain medications[[2]].
Advertisement
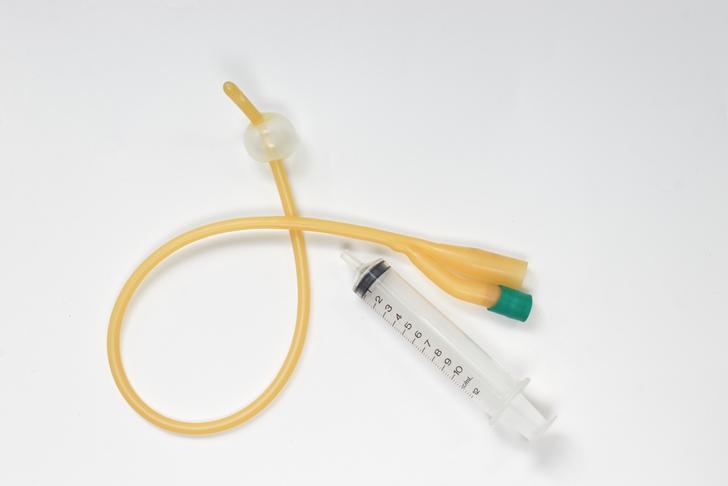
Catheter Use
Catheters, which are tubes inserted into the bladder to drain urine, can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract and increase the risk of UTIs. Long-term catheter use is a common cause of UTIs in hospitalized patients and those with chronic medical conditions[[1]].
Advertisement
Weakened Immune System
A weakened immune system can make it more difficult for your body to fight off infections, including UTIs. Conditions that can weaken the immune system include diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and certain medications, such as corticosteroids and chemotherapy drugs[[2]].

Advertisement
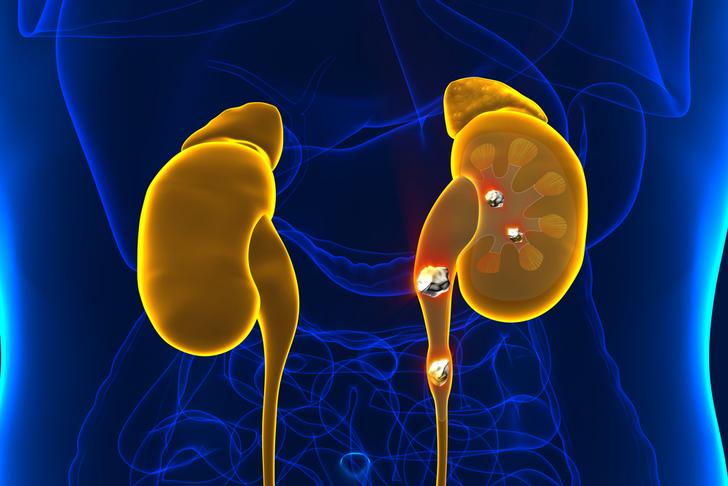
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can obstruct the flow of urine and create an environment where bacteria can thrive, increasing the risk of UTIs. If you have a history of kidney stones, it is important to work with your healthcare provider to develop a prevention plan[[3]].
Advertisement
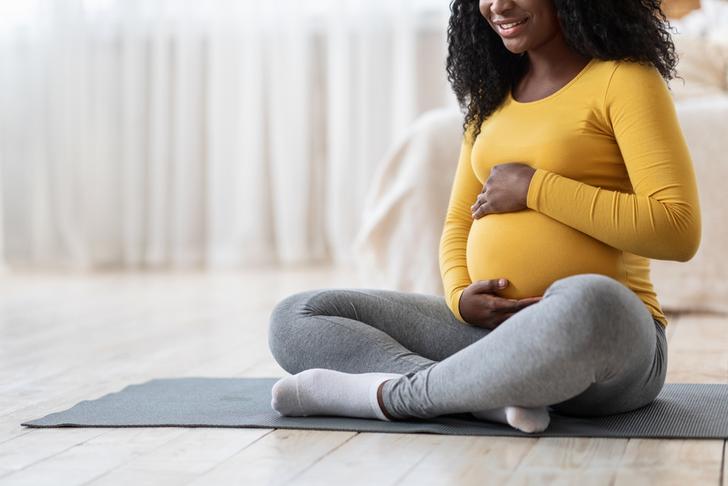
Pregnancy
Pregnant women are at an increased risk of UTIs due to hormonal changes and the pressure of the growing uterus on the urinary tract. It is important for pregnant women to be screened for UTIs and receive prompt treatment if an infection is detected[[1]].

Advertisement
Menopause
Menopause can cause changes in the urinary tract that make women more susceptible to UTIs. Decreased estrogen levels can lead to thinning of the urinary tract lining and reduced ability to fight off bacteria[[2]].

Advertisement
Use of Spermicides or Diaphragms
The use of spermicides or diaphragms for contraception can increase the risk of UTIs. Spermicides can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina, while diaphragms can put pressure on the urethra and make it more difficult to completely empty the bladder[[1]].

Advertisement
Constipation
Constipation can cause pressure on the urinary tract, making it more difficult to empty the bladder and increasing the risk of UTIs. Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and exercising regularly can help prevent constipation[[2]].

Advertisement
Poor Hygiene
Poor hygiene can introduce bacteria into the urethra and increase the risk of UTIs. It is important to practice good hygiene by wiping front to back after using the toilet, keeping the genital area clean, and changing underwear daily[[1]].

Advertisement
Symptoms of a UTI
Below are some common symptoms of a UTI:
Urinary urgency and frequency: People may experience a strong and frequent urge to urinate.
Burning sensation: Pain or a burning sensation during urination is a common symptom of a UTI.
Cloudy or bloody urine: UTIs can cause urine to appear cloudy, dark, or have a strong odor. In some cases, blood may be visible in the urine.
Lower abdominal or pelvic pain: Persistent discomfort or pressure in the lower abdomen or pelvis can indicate a UTI.
Fatigue and general malaise: Some individuals may experience fatigue, general weakness, or feeling unwell.
Advertisement
Treatments
Here are some common treatments for UTIs:
Antibiotics: The primary treatment for UTIs is a course of antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection. The specific antibiotic and duration of treatment will depend on the type and severity of the infection. Individuals need to complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed.
Increased fluid intake: Drinking plenty of water and fluids can help flush bacteria from the urinary system and promote healing. Cranberry juice or supplements may also have a preventive effect, but their effectiveness in treating UTIs is limited.
Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate discomfort or pain during urination.
Urinary analgesics: Healthcare providers may prescribe urinary analgesics to help relieve urinary pain and discomfort.
Preventive measures: To prevent recurrent UTIs, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids, urinate regularly, and practice good hygiene habits, including wiping from front to back after using the toilet.
Catheter care: If a UTI is related to using urinary catheters, proper catheter care, and maintenance are essential to reduce the risk of infection.
Advertisement
Conclusion
In conclusion, knowledge about the causes, symptoms, and treatments for urinary tract infections (UTIs) empowers individuals to take proactive steps to maintain a healthy urinary system. Adopting good hygiene practices, managing underlying medical conditions, and being mindful of risk factors can minimize the likelihood of developing a UTI.
However, should symptoms arise or there is suspicion of a UTI, seeking timely medical attention is crucial. Proper diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications, and a swift recovery can be achieved. Remember, UTIs are common but treatable infections, and healthcare professionals’ guidance ensures appropriate care and management.
By staying informed and proactive, individuals can safeguard their urinary health and enjoy a better quality of life. Be attentive to your body’s signals, maintain good hygiene, and seek medical assistance when needed.
Advertisement