10 esophageal cancer symptoms
 Article Sources
Article SourcesEsophageal cancer ranks number six worldwide as the cause of cancer deaths.[[2]] It starts in the tube connecting the throat to the stomach and can happen at any point along the esophagus. It’s more common in men and in people who use tobacco and alcohol. Esophageal cancer symptoms often don’t show up until the disease is advanced. Many of the symptoms are subtle at first and appear as changes in digestion. They’re often things that can happen without underlying issues, but the symptoms of esophageal cancer typically get worse as the disease progresses.
Difficulty Swallowing
One of the most common and distinct esophageal cancer symptoms is difficulty swallowing, also called dysphagia.[[5]] This happens as the cancer grows larger and partially blocks the esophagus. It’s often one of the first symptoms. When this symptom happens, it can feel like food is getting stuck either in the throat or in the chest. It can be worse when eating certain foods like bread and meat. The feeling can get worse over time as the tumor grows and restricts the esophagus even more.

Advertisement
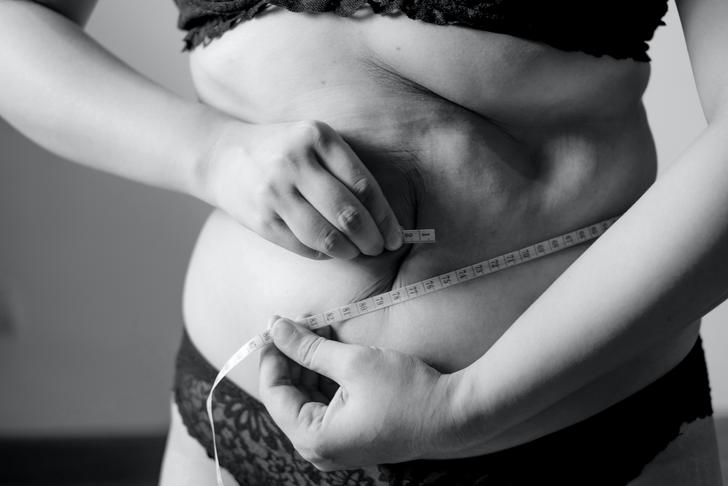
Unintentional Weight Loss
The swallowing issues can sometimes lead to unintentional weight loss. Someone experiencing painful or difficult swallowing might eat less, choose softer foods, or switch to a liquid diet to avoid the issue. They might also decrease how much they eat. These dietary changes can cause weight loss. Esophageal cancer can also decrease the appetite. At the same time, it can increase metabolism.[[5]] The higher metabolism combined with less food consumption often causes weight loss.

Advertisement
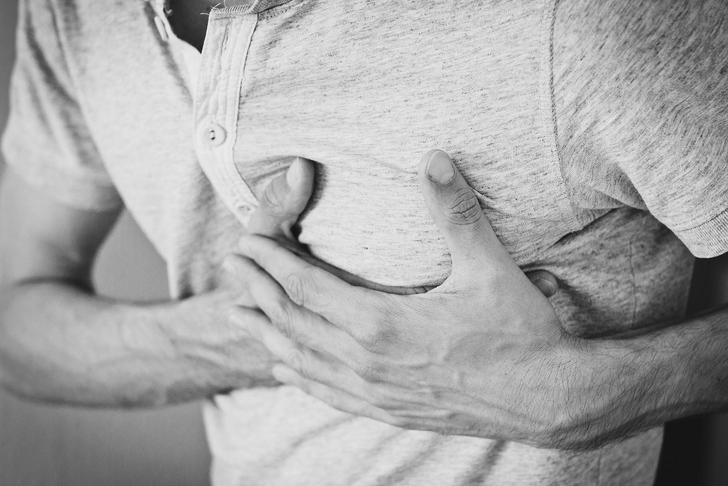
Chest Pain
Another common symptom of esophageal cancer is pain or discomfort in the chest. This sensation typically happens in the middle of the chest, often behind the breastbone. It might be associated with swallowing due to the narrowing esophagus. This symptom can also feel like pressure or burning in the chest.[[5]] It’s possible to have discomfort in the chest for other reasons. While heartburn can be another esophageal cancer, it’s also common to have heartburn without cancer, which can cause the burning feeling.

Advertisement
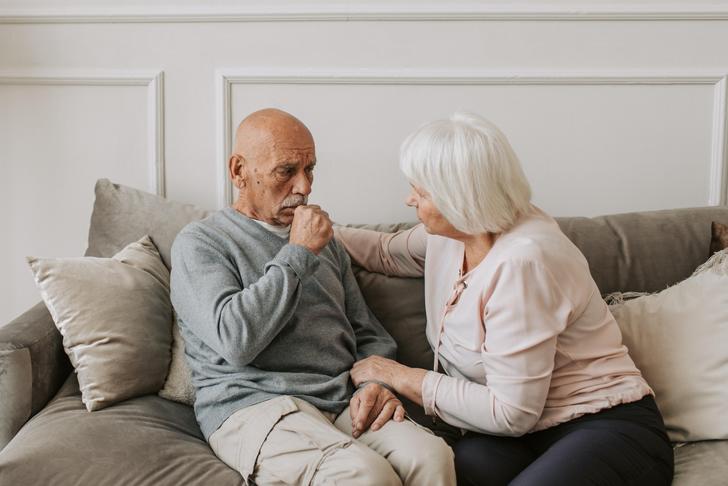
Chronic Cough
Some people with esophageal cancer have a chronic cough. This type of cancer sometimes causes excessive mucus or bleeding. These symptoms of esophageal cancer can cause coughing. If the tumor grows large enough, it can cause the esophagus to touch the trachea, which can also cause coughing.[[6]] Several conditions can cause coughing, including heartburn, asthma, bronchitis, and COPD. A persistent cough, especially if there’s no known underlying cause, is something a doctor should check out to rule out esophageal cancer.

Advertisement
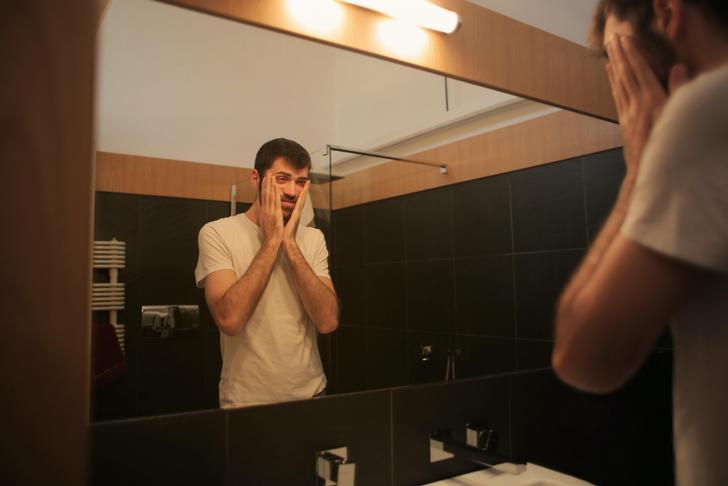
Vomiting
Vomiting is sometimes an esophageal cancer symptom. People with esophageal can also vomit blood because the cancer sometimes causes bleeding. Blood in the stomach can come up with vomit and may be visible.[[6]] Also, sometimes treatments for esophageal cancer can cause vomiting as a side effect. Some people might also regurgitate undigested food. This can happen if the food can’t pass through the narrowed esophagus. The food might come back up the esophagus in this case.

Advertisement
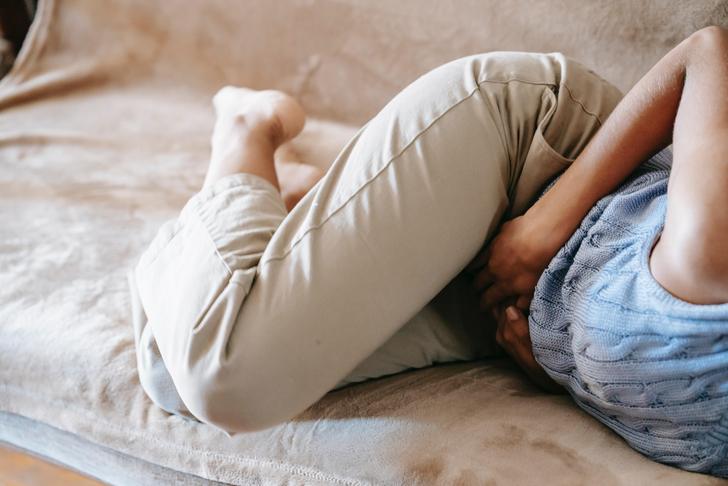
Indigestion or Heartburn
Heartburn is common for many people occasionally, but frequent indigestion can cause issues in the esophagus. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can increase the risks of esophageal cancer.[[7]] The frequent acids going into the esophagus can cause the lining to change as a protection method, resulting in Barrett’s esophagus. This can eventually grow into esophageal cancer. Indigestion or heartburn that gets worse over time could be an esophageal cancer symptom.[[2]] Individuals should let their doctors know if heartburn gets worse or happens more frequently.

Advertisement
Dark Stools
When someone has esophageal cancer, they might experience bleeding in the esophagus. Because the bleeding happens internally, it’s not always obvious. However, the person’s stools can offer a clue about bleeding. Stools often appear black and tarry if there’s blood present. It might also have a foul smell. This stool appearance indicates the bleeding is happening in the upper digestive tract including the esophagus, stomach, or beginning of the small intestine. It gets darker as it moves through the digestive system.[[1]]

Advertisement
Hoarseness
Changes to the voice, especially hoarseness, can be a symptom of esophageal cancer. The voice might sound raspy or strained. This happens if the cancer impacts the vocal cords and affects the laryngeal nerves.[[6]] Hoarseness can happen due to minor issues such as colds, laryngitis, GERD, and overusing the voice.[[4]] These instances of hoarseness might go away after the issue resolves. It can also be a sign of other types of cancer including lung cancer and laryngeal cancer.

Advertisement
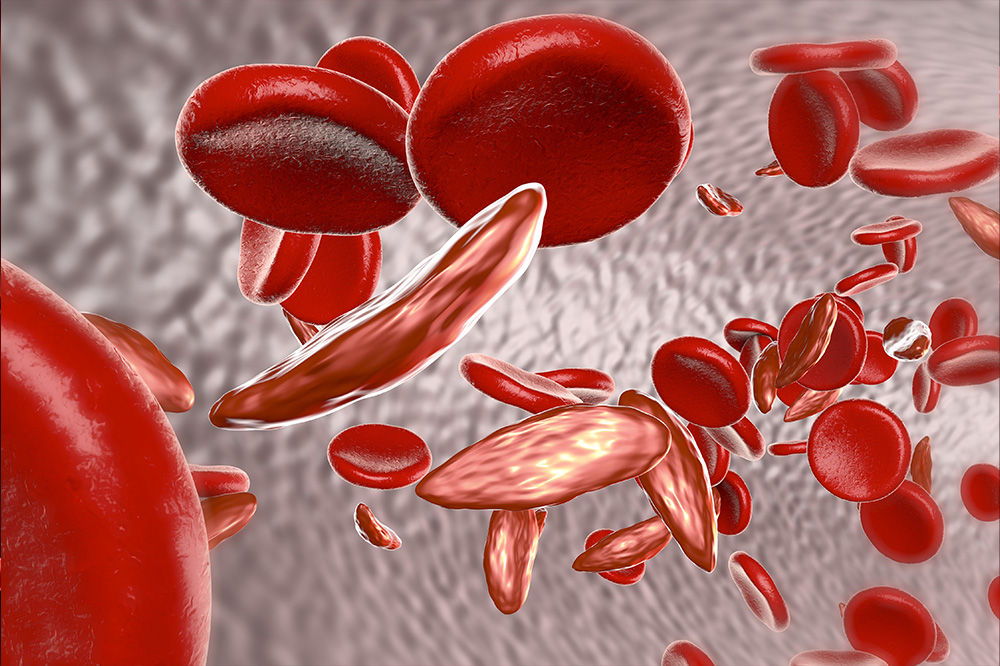
Anemia
Bleeding in the esophagus due to esophageal cancer can cause anemia. This happens when the patient has low healthy red blood cell levels.[[5]] The bleeding can cause the person to lose more red blood cells than their body replaces. It can also cause the person to feel tired. Other situations can also cause anemia including deficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid. Medical conditions that can result in anemia include Crohn’s disease, kidney disease, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Advertisement
Pain in Other Areas
If esophageal cancer spreads to other nearby areas, the patient might experience pain in those areas. If it spreads to the membrane around the heart or between the lungs, it can cause back pain.[[3]] Esophageal cancer can also spread to the bones. This can cause bone pain or achiness. It can also spread to other areas and cause pain such as headaches if it spread to the brain or abdominal pain if it spreads to the liver.[[6]]

Advertisement