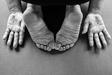
10 Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. It can also impact other body systems, leading to a variety of symptoms. In this article, we will discuss 10 common symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis to help you better understand this condition.
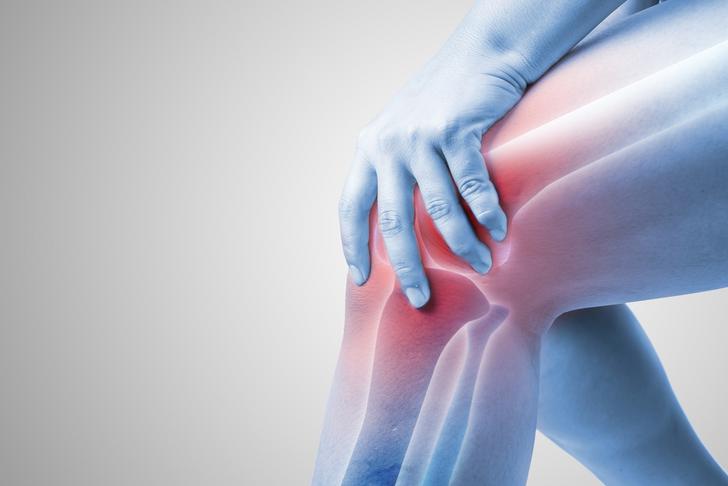
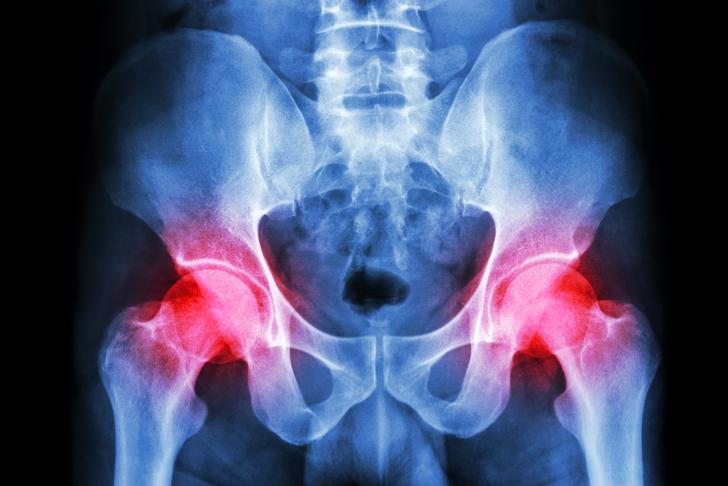
Joint Pain
Joint pain is one of the most common symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. It is usually a result of inflammation in the joint lining, which can cause swelling, warmth, and tenderness[[1]]. Pain is often worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
Advertisement
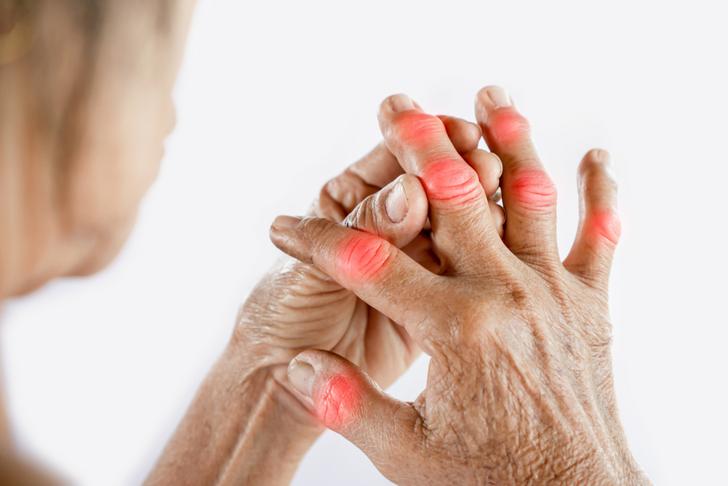
Joint Swelling
Swelling is another common symptom of RA, as the inflamed joint lining produces excess fluid. This can lead to visibly swollen and tender joints, particularly in the hands, wrists, and knees[[2]].

Advertisement
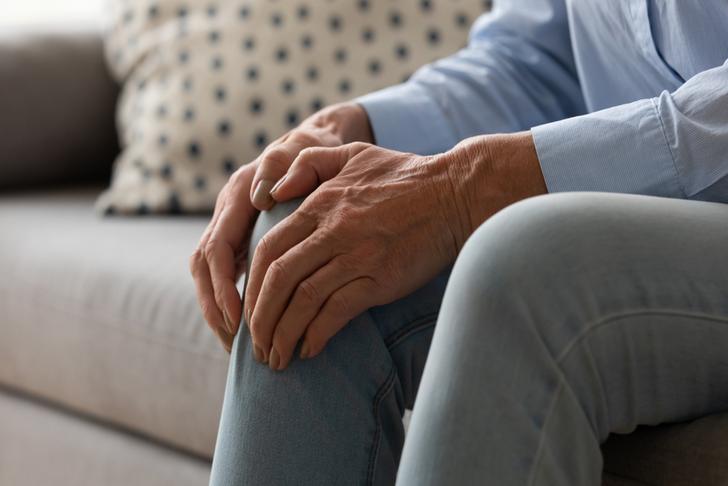
Joint Stiffness
Stiffness in the joints is a common complaint among those with rheumatoid arthritis. It is often most noticeable in the morning or after periods of inactivity, and can last for several hours[[1]].

Advertisement
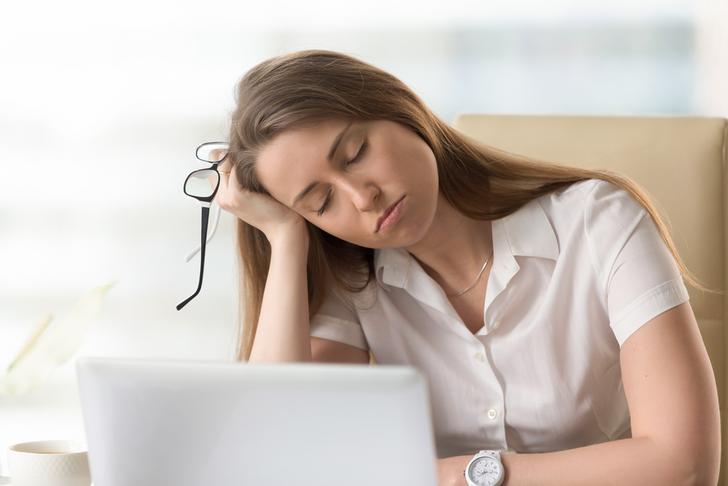
Fatigue
Fatigue is a common symptom of RA, as the body’s immune system is constantly working to fight inflammation. This can leave individuals feeling tired and lacking energy, even after a full night’s sleep[[2]].

Advertisement
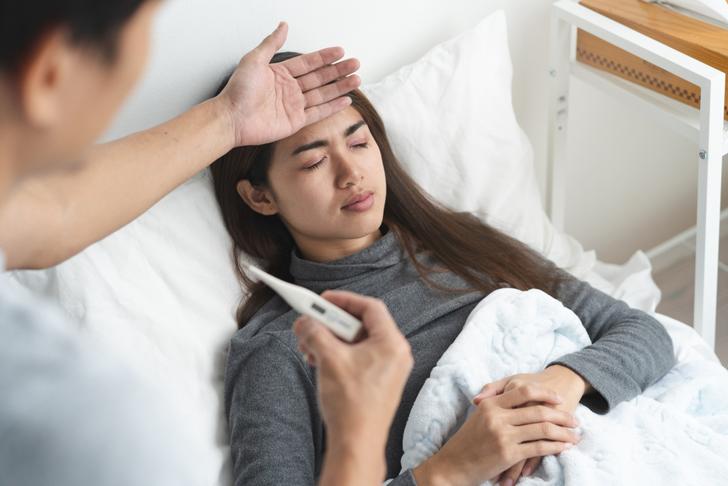
Fever
A low-grade fever may accompany rheumatoid arthritis, particularly during periods of increased inflammation. This is a result of the body’s immune response to the disease[[3]].

Advertisement
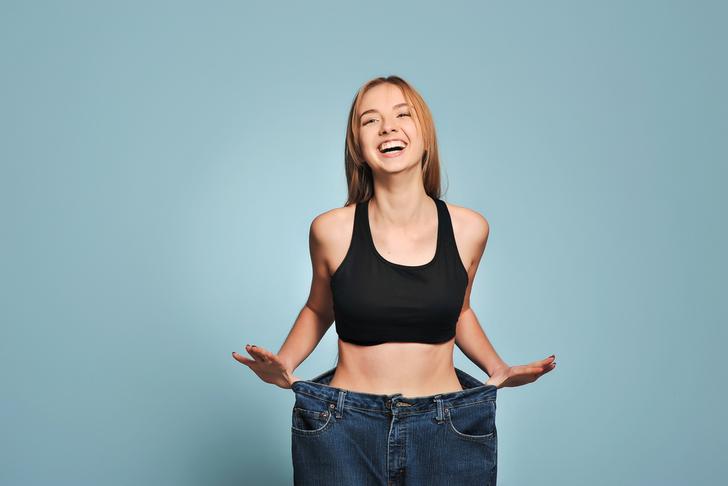
Weight Loss
Unintentional weight loss can be a symptom of rheumatoid arthritis, as the body uses more energy to fight inflammation. Additionally, pain and stiffness may make it difficult to prepare and consume meals, leading to a decreased appetite[[2]].

Advertisement
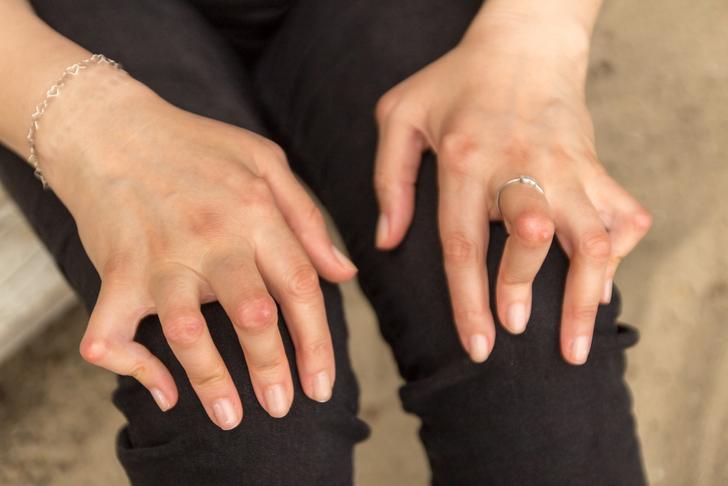
Rheumatoid Nodules
Some individuals with RA may develop rheumatoid nodules, which are firm lumps that form under the skin. These nodules typically appear near joints affected by the disease, such as the elbows, fingers, and knees[[3]].

Advertisement
Anemia
Anemia, or a low red blood cell count, is a common symptom of rheumatoid arthritis. This can result from the body’s immune system attacking healthy red blood cells, or from a decreased production of these cells due to inflammation[[3]].
Advertisement
Dry Eyes and Mouth
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect the glands that produce tears and saliva, leading to dry eyes and mouth. This is known as Sjögren’s syndrome, which is an autoimmune disorder that often occurs alongside RA[[2]].

Advertisement
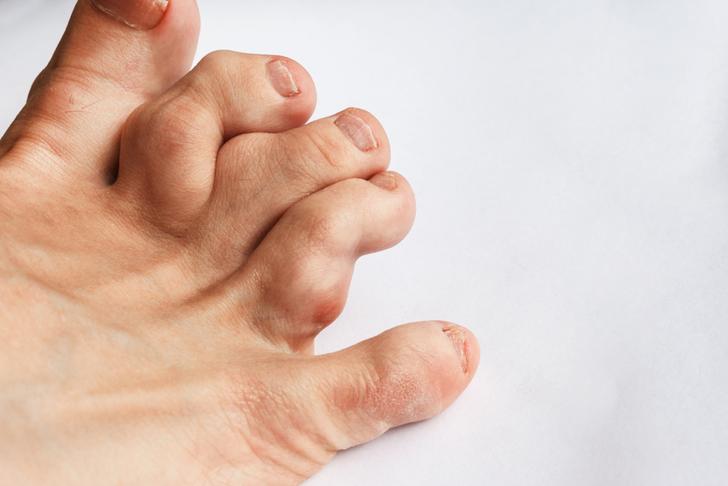
Joint Deformity
Over time, the inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis can damage the joints and surrounding tissues, leading to joint deformity. This can result in a loss of function and mobility, as well as changes in the appearance of the affected joints[[1]].
Advertisement
Conclusion
In conclusion, rheumatoid arthritis is a complex autoimmune disease affecting joints and other body systems. By understanding the common symptoms of RA, individuals can better recognize the condition and seek appropriate medical care. If you suspect you may have rheumatoid arthritis, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
It’s important to note that rheumatoid arthritis symptoms often overlap with other conditions. Osteoarthritis, lupus, and fibromyalgia are among the conditions that may present with similar symptoms, making it crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure an accurate diagnosis. Early diagnosis and intervention can help prevent joint damage and improve the overall quality of life for those affected by RA.
In terms of treatment, there are several options available to manage rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and slow down disease progression. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to decrease inflammation and relieve pain. Corticosteroids may be prescribed to control severe inflammation, typically for short periods, due to potential side effects. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are increasingly being used to slow the progression of RA, and biologic agents, which target specific aspects of the immune system, may also be utilized.
Physical and occupational therapy can also benefit RA patients, helping them maintain joint function and mobility. Incorporating low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or yoga into a daily routine can relieve pain and improve overall well-being. Support from friends, family, and support groups can be invaluable in coping with the emotional challenges that may arise from living with a chronic condition like RA.
Dietary factors can also play a role in managing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Although there is no specific “rheumatoid arthritis diet,” a balanced and nutritious diet can benefit overall health and support the immune system. Some individuals may find that certain foods exacerbate their symptoms – common culprits include red meat, dairy, and gluten – and identifying and avoiding these triggers can relieve them. Ensuring an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acids in fatty fish and certain plant sources may help reduce inflammation.
Ultimately, managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively requires a comprehensive approach that considers all aspects of an individual’s health, including physical, emotional, and nutritional factors. By staying informed about the condition and working closely with a healthcare professional, patients can develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to their needs and preferences. Education and self-advocacy are key to living well with rheumatoid arthritis.
Advertisement