10 Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can lead to nerve compression and pain. This article will explore 10 common symptoms of spinal stenosis, helping you to better understand this condition and recognize its signs.
Pain in the Back or Neck
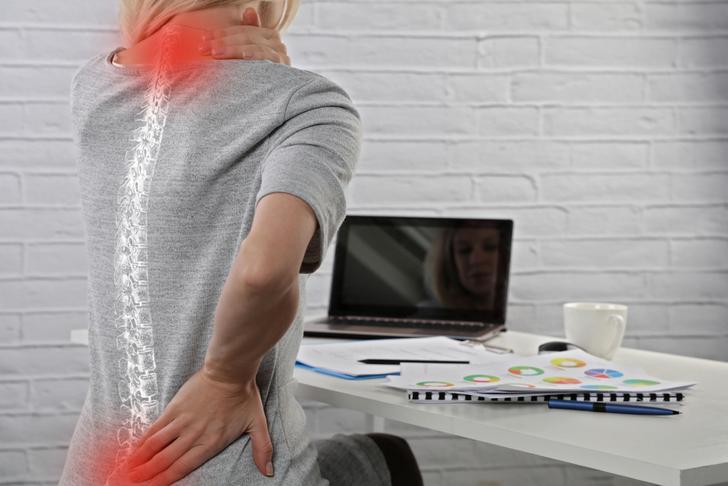
One of the most common symptoms of spinal stenosis is pain in the back or neck. This pain can be sharp, dull, or aching, and may worsen with certain activities or positions[[1]].
Advertisement
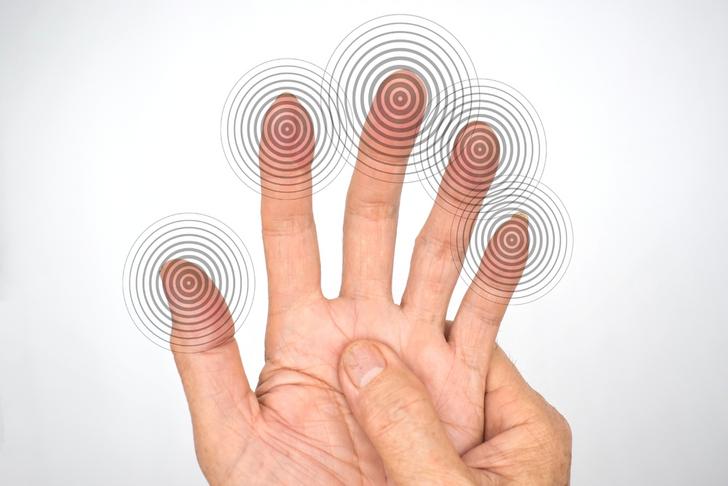
Numbness or Tingling
Numbness or tingling in the arms, legs, hands, or feet is another common symptom of spinal stenosis. This can be caused by the compression of nerves in the spinal canal[[2]].

Advertisement
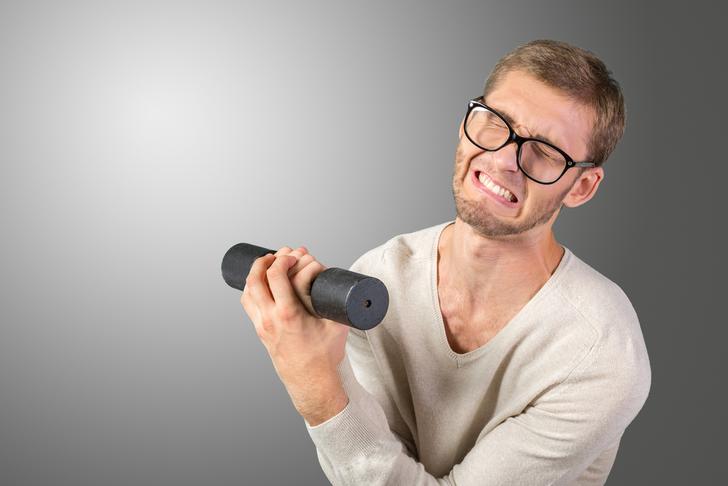
Muscle Weakness
Muscle weakness in the arms or legs can also be a sign of spinal stenosis. This weakness may make it difficult to perform everyday tasks, such as lifting objects or walking[[2]].

Advertisement
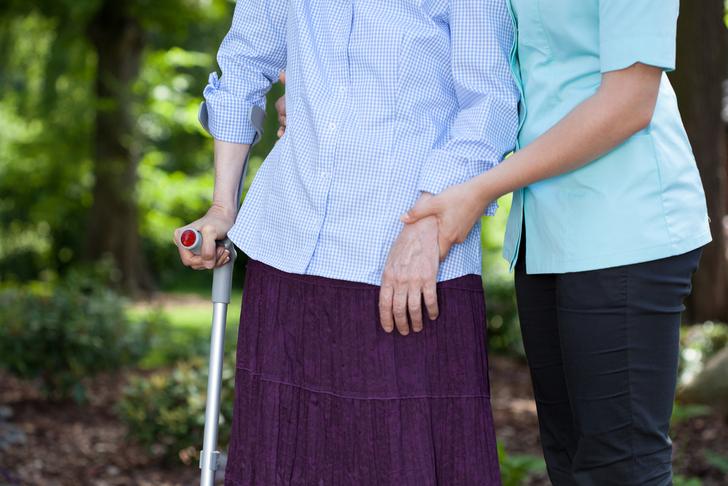
Difficulty Walking
Difficulty walking or maintaining balance can be a symptom of spinal stenosis, particularly when it affects the lower back (lumbar stenosis). This can result in a feeling of unsteadiness or a tendency to stumble[[1]].

Advertisement
Loss of Bladder or Bowel Control
In severe cases of spinal stenosis, the compression of nerves can lead to a loss of bladder or bowel control. This is a rare but serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention[[3]].

Advertisement
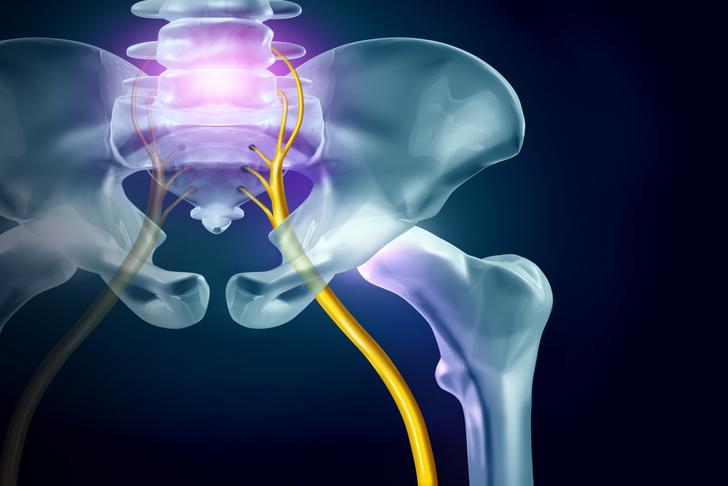
Sciatica
Sciatica, or pain that radiates from the lower back down the leg, can be a symptom of lumbar spinal stenosis. This pain is often described as sharp, burning, or shooting, and may be accompanied by numbness or tingling[[1]].
Advertisement
Cramping or Spasms
Muscle cramping or spasms in the arms or legs can be another symptom of spinal stenosis. These spasms may be triggered by certain activities or positions, and can cause significant discomfort[[2]].

Advertisement
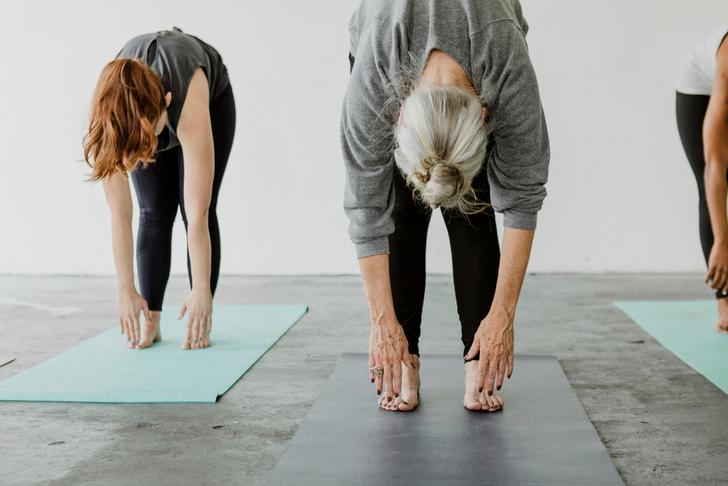
Pain that Improves with Bending Forward
A unique symptom of spinal stenosis is pain that improves when bending forward. This position can help to relieve pressure on the nerves in the spinal canal, providing temporary relief from pain[[1]].

Advertisement
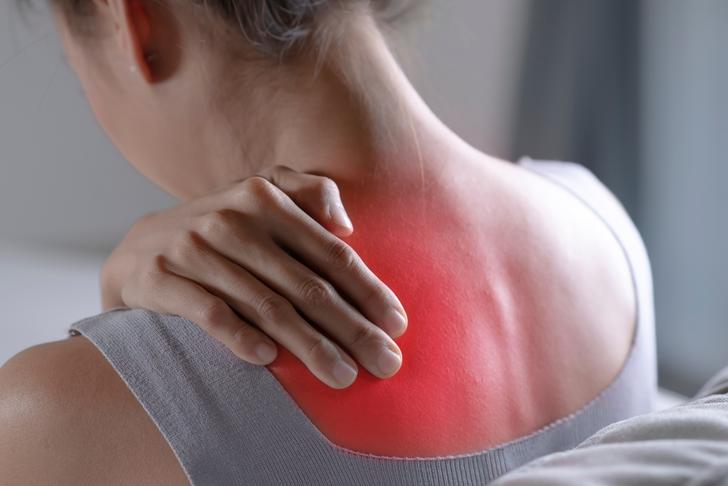
Stiffness
Stiffness in the back or neck can be a sign of spinal stenosis. This stiffness may be worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity, and can make it difficult to move or perform daily tasks[[2]].
Advertisement
Fatigue
Fatigue or a general feeling of tiredness can be a symptom of spinal stenosis. This can be caused by the body’s efforts to cope with pain and discomfort, as well as the reduced ability to perform daily activities[[3]].

Advertisement
Causes of Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spaces within your spine, which can put pressure on the nerves that travel through the spine. It typically occurs in the lower back and the neck and is often caused by:
- Age: Spinal stenosis is most commonly due to changes in the spine related to osteoarthritis. As you get older, your body’s connective tissues can thicken and harden, and bones and joints may enlarge.
- Herniated Discs: The soft cushions that act as shock absorbers between your vertebrae can dry out with age. Cracks in the discs can allow the soft inner material to escape and press on the spinal cord or nerves.
- Spinal Injuries: Trauma to your spine can cause fractures or dislocations of one or more vertebrae. These can damage the spinal canal. Swelling of nearby tissue immediately after back surgery also can put pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Advertisement
Treatments for Spinal Stenosis
Treatment for spinal stenosis depends on the location and severity of the condition. It’s typically aimed at relieving symptoms and improving the patient’s ability to function. The treatment options include:
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and sometimes opioids can be used to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises can help to improve balance, strength, and flexibility. A physical therapist can design a program to meet your specific needs.
- Steroid Injections: Injecting a corticosteroid around the impingement can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Surgery: If other treatments aren’t helping, surgery can be performed to create more space for the nerves or spinal cord.
Advertisement
Conclusion
Spinal stenosis can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain, depending on its severity and location. Recognizing these symptoms and seeking professional medical advice is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. With the appropriate treatment, including medication, physical therapy, or potentially surgery, patients with spinal stenosis can manage their symptoms and maintain their quality of life. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect that you or a loved one may be experiencing symptoms of spinal stenosis.
Advertisement