11 Tips to Prevent Heart Attack
Heart attacks are a leading cause of death worldwide, but many cases can be prevented through lifestyle changes and medical interventions. In this article, we’ll explore 11 tips to help you reduce your risk of heart attack and maintain a healthy cardiovascular system.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can contribute to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, all of which increase your risk of heart attack[[1]]. Aim for a body mass index (BMI) within the normal range and consult with your healthcare provider to determine your ideal weight.

Advertisement
Exercise Regularly
Engaging in regular physical activity can help lower your risk of heart attack by improving your cardiovascular fitness, reducing blood pressure, and helping you maintain a healthy weight[[1]]. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.

Advertisement
Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help lower your risk of heart attack[[3]]. Limit your intake of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars to support heart health.

Advertisement
Don’t Smoke
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart attack, as it damages your blood vessels and increases your risk of blood clots[[1]]. If you smoke, quitting is one of the best things you can do for your heart health.

Advertisement
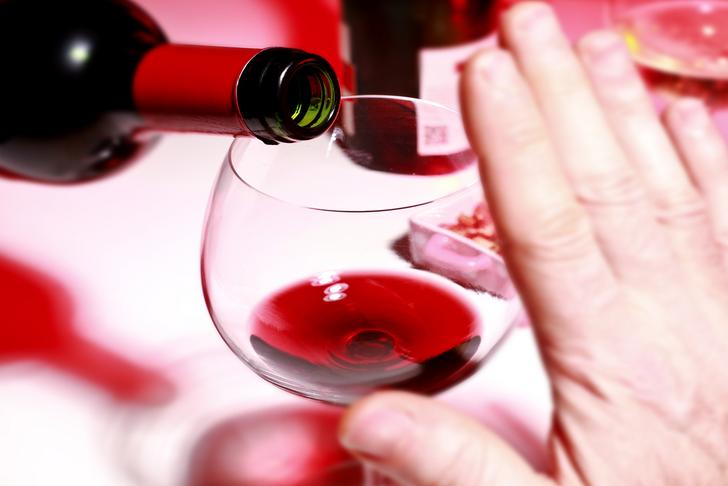
Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can raise your blood pressure and contribute to heart disease[[1]]. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation: up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.

Advertisement
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure and other heart attack risk factors[[1]]. Find healthy ways to cope with stress, such as exercise, meditation, or talking to a mental health professional.

Advertisement
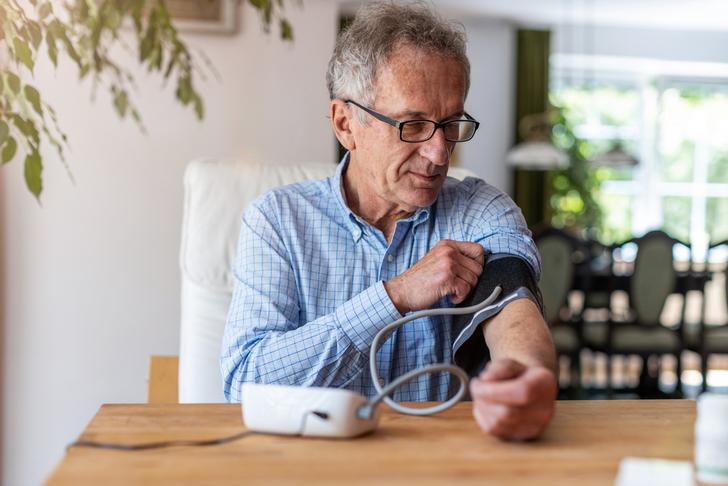
Monitor Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart attack, but it often has no symptoms[[1]]. Regularly check your blood pressure and work with your healthcare provider to manage it if it’s consistently high.

Advertisement
Control Cholesterol
High cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in your arteries, increasing your risk of heart attack[[1]]. Get your cholesterol levels checked regularly and work with your healthcare provider to manage them through diet, exercise, and medication if necessary.

Advertisement
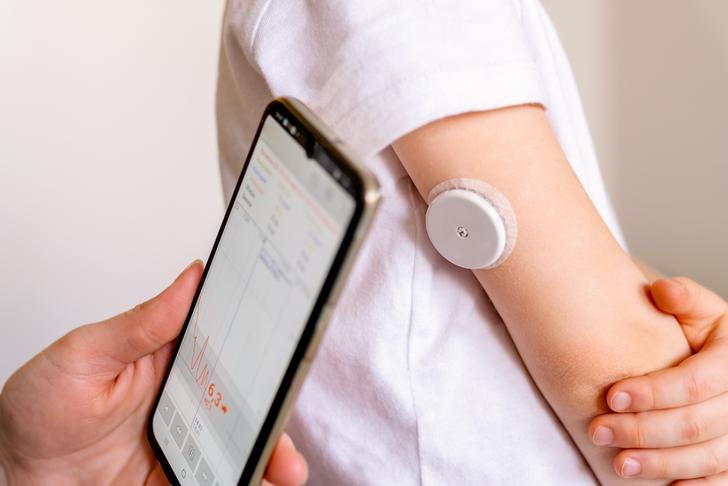
Manage Diabetes
Diabetes significantly increases your risk of heart attack[[1]]. If you have diabetes, work with your healthcare provider to manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of heart disease.

Advertisement
Take Medications as Prescribed
If you have high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or other heart attack risk factors, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to help manage them[[1]]. Be sure to take your medications as directed and discuss any concerns or side effects with your healthcare provider.
Advertisement
Get Regular Checkups
Regular checkups with your healthcare provider can help identify and manage heart attack risk factors before they become serious problems[[1]]. Be proactive about your heart health and schedule regular appointments with your healthcare provider.

Advertisement
Symptoms of a Heart Attack
The following are the typical symptoms of a heart attack:
Chest Discomfort: This is often described as pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center of the chest that lasts for more than a few minutes or goes away and comes back.
Discomfort in Other Areas of the Upper Body: This can include pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
Shortness of Breath: This can occur with or without chest discomfort.
Other Signs: Other symptoms may include breaking out in a cold sweat, nausea, or lightheadedness. In some cases, particularly in women, symptoms may be more subtle, like unexplained fatigue, sudden dizziness, or gastric discomfort.
Advertisement
Causes of a Heart Attack
Heart attacks usually result from coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition in which a waxy substance called plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries that supply oxygen-rich blood to your heart. A heart attack occurs when an area of plaque ruptures, causing a blood clot to form and block blood flow through the artery. If the blood flow isn’t restored quickly, the section of heart muscle fed by the artery begins to die.
Risk factors for CAD and heart attack include:
- Age
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol or triglyceride levels
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Unhealthy diet
- High blood sugar, often linked to diabetes
- Family history of heart disease
Advertisement
Treatments for a Heart Attack
Treatments for a heart attack aim to restore blood flow to the heart muscle as quickly as possible to prevent further heart muscle damage. This can include:
Medications: Various medications can be used, including aspirin, thrombolytics (“clot-busting” drugs), antiplatelet drugs, anticoagulants, pain relievers, nitroglycerin, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors.
Medical Procedures: In some cases, medical procedures are needed to restore blood flow, such as coronary angioplasty and stenting or coronary artery bypass surgery.
Lifestyle Changes and Cardiac Rehabilitation: After a heart attack, lifestyle changes and cardiac rehab programs, including exercise training, education on heart-healthy living, and counseling to reduce stress, are recommended.
Advertisement
Conclusion
Taking steps to maintain a healthy lifestyle is crucial in preventing heart attacks. These steps include quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, eating a heart-healthy diet, managing diabetes if you have it, and reducing stress. Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack—such as chest discomfort, discomfort in other areas of the upper body, shortness of breath, and other signs like cold sweats, nausea, or lightheadedness—is vital for seeking prompt medical attention. Treatments for a heart attack aim to restore blood flow to the heart muscle as quickly as possible and may include medications, medical procedures, and lifestyle changes. By following these preventative measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of a heart attack and promote a healthier, happier heart.
Advertisement